In the quest for new energy sources with low or no greenhouse gas emissions, marine energies have a high potential. Different types of marine energy exist, from offshore wind turbines to tidal turbines, not forgetting ocean thermal energy. The wide variety of marine renewable energy (MRE) harvesting systems are at very staggered degrees of technological maturity.
To ensure the harmonious development of this new use of the world's oceans, close collaboration is required with the other users of the sea, while remaining aware of all their environmental and social impacts.
Offshore wind power
The wind is far stronger at sea than on land. It sweeps across vast unobstructed stretches. Offshore wind turbines harness wind power to convert it into electricity. In this context, the term "offshore" is employed simply in opposition to the term "onshore", without any implication of distance from the coast. Offshore wind turbines function based on the same principle as conventional onshore models: they use the wind's kinetic energy and transform it into electricity. They are therefore wind-powered electrical generators.

©photo
Wave power
Wave power refers to the production of electric energy from swell, i.e. successive waves caused by wind passing over the sea surface and sometimes spreading across very long distances.

©flickr/aquamarinepowerltd
Marine current power
Tidal stream generators are designed to convert the kinetic energy of marine currents into electricity.
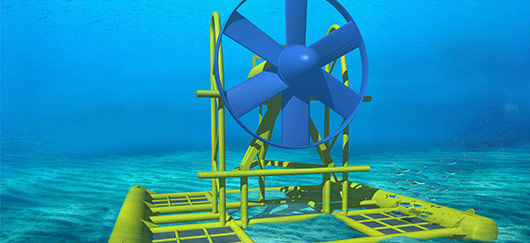
(©Sabella)
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC)
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion uses differences in temperature in the ocean between surface waters and deeper waters to produce electricity.

©DCNS
Osmotic power
Osmotic power refers to the energy obtained from the difference in salinity between seawater and freshwater, which are separated by a semi-permeable membrane. It involves using the level or pressure created by the migration of molecules through the membrane. The resulting water pressure is used to turn a turbine to produce electricity.

©Statkraft
Tidal power
Tidal power consists in harnessing the energy of tides in coastal areas with a high tidal range (large difference between high tide and the succeeding low tide). The phenomenon of tides is induced by the gravitational forces exerted on the ocean by the Moon and the Sun.

©EDF-Yannick Le Gal
